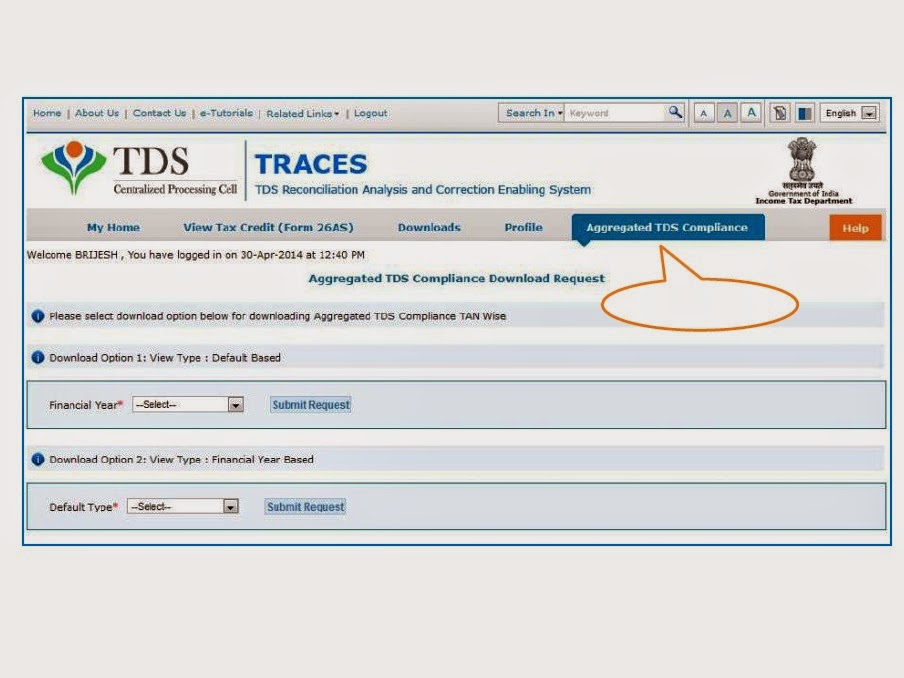
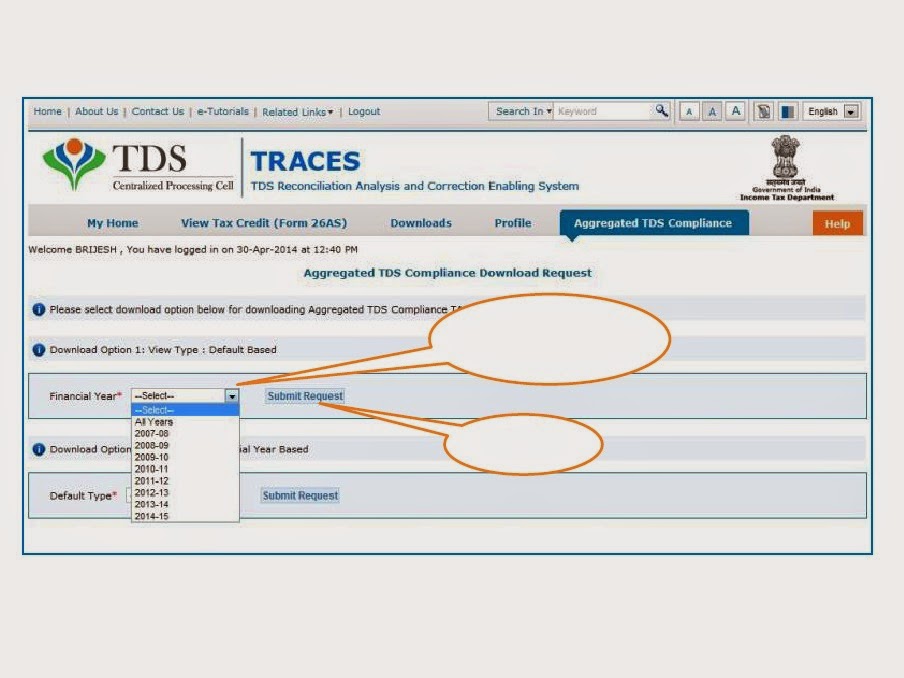
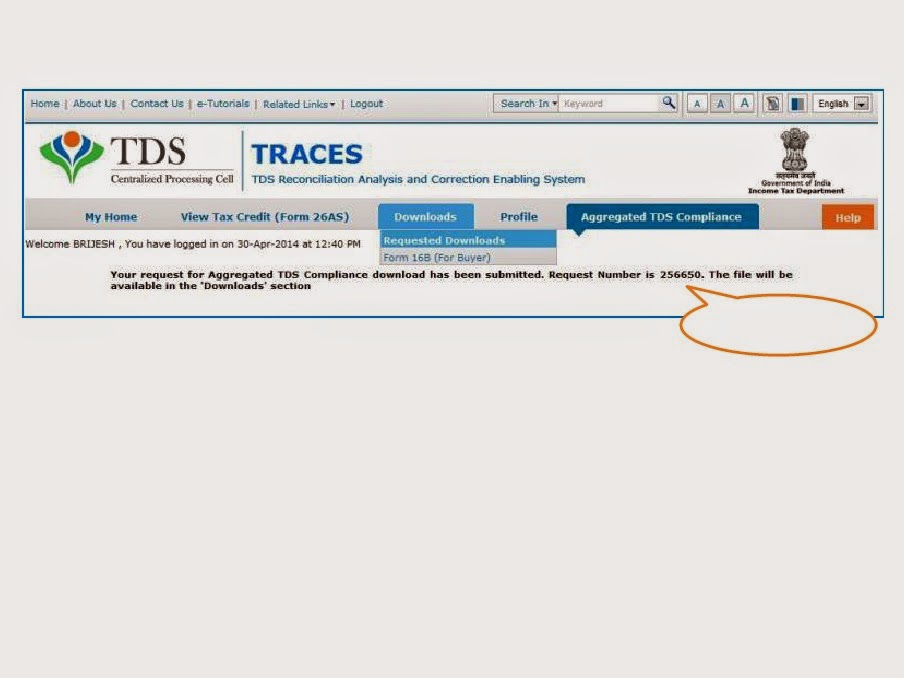
While one endeavors to derive income, the possibility of incurring losses cannot be ruled out. Based on the principles of natural justice, a set-off should be available for loss incurred. The income tax laws in India recognise this and provide for adjustment and utilisation of the losses. However, there are conditions which have been introduced to prevent misuse of such provisions.
To the common taxpayer, income tax is a crunch into the income earned. Accordingly, awareness of the relevant provisions pertaining to set off and carry forward of losses is essential in order to maximize tax benefits. The relevant provisions have been summarised here:
A) Set off of loss under the same head of income.(section 70) (Intra-head set off)
Income of a person is computed under five heads. ‘Sources’ of income derived by an individual may be many but yet they could be classified under the same head. For instance, an individual may have a dual employment, yet the income would be classified under the head ‘Salaries’. However, given the mechanism of computing taxable salary income, it would be safe to say that an individual cannot incur losses under this head of income.
Consider a situation where Harsh has two properties – one, occupied by him and the other, let out. Harsh pays interest on loan of Rs 1.50 lakh on the property occupied and derives net rental income of Rs 1.50 lakh from the let-out property. In case of a self-occupied property, income is computed as nil and interest expenditure results in loss. The loss of Rs 1.50 lakh can be set off against rent income of Rs 1.50 lakh; the income chargeable under the head ‘House property’ will be ‘Nil’.
An exception to intra head set off is loss under the head ‘Capital gains’, which may arise from transfer of any capital asset. Long-term capital loss arises from transfer of shares or units where holding period is more than 12 months and in respect of other assets holding period is more than 36 months prior to sale. Transfer of assets held for less than prescribed period results in short-term capital loss. Long-term capital loss cannot be set off against short-term capital gains.
Further, loss incurred from speculation loss (eg. from shares or commodities) cannot be set off against any other income.
Also, it is unlikely that the benefit of set off of loss under an activity or source will be available, where the income from an activity or source is exempt from taxation.
Summary of exceptions to Intra-head set off:
1. Loss from speculation business cannot be set of against profit from an non speculation business
(Interpretation: Loss from non speculative business can be set-off against speculation income)
2. LTCL can only be set off against LTCG and cannot be set off against STCG
(Interpretation: STCL can be set off against LTCG)
3. No loss can be set-off against casual income i.e. Income from lotteries, cross word puzzles, betting gambling and other similar games.
4. No expenses can be claimed against casual income
5. Loss from the activity of owning and maintaining race horses cannot be set off against other incomes
6. Loss from an exempted source cannot be set off
(e.g. Share of loss of firm, agricultural losses, cultivation expenses)
B) Set off Loss from one head against Income from another Head (Inter head set off)
A person may have various sources of income computed under different heads of income. Loss under one head of income is generally allowed to be set off against income under another head.
For instance, X has only one property, which is occupied by him and the loss is Rs 1.50 lakh. He derives salary of Rs 10 lakh during the year. Here, he can set off the loss of Rs 1.50 lakh against his salary income by making appropriate declarations to his employer, thereby making his net taxable income Rs 8.50 lakh.
Certain exceptions to the provisions are that the loss from business or profession cannot be set off against salary income. Capital loss, whether long term or short term, can be set off only against capital gains income.
Where during a given year, there is no sufficient income to absorb the loss, unabsorbed loss can be carried forward and set off against income, in the future years as explained here.
Summary of exceptions to Inter-head set off:
1. Loss from speculation cannot be set of against any other head.
(Interpretation: Loss from other heads can be set-off against business income.)
For Example: House property loss can be set-off against Speculative Incomes but speculation loss cannot be set off against House property)
2. Business loss cannot be set-off against salary income. (It can be set-off against other incomes)
Loss under the head Capital Gains (LTCL or STCL) cannot be set-off against any other head.
(Interpretation: Loss from other heads can be set-off against Capital Gains)
For Example: HP loss can be set-off against CG but LTCL or STCL cannot be set off against HP
4. No loss can be set-off against casual income
5. No expenses can be claimed against casual income
6. Loss from the activity of owning and maintaining race horses cannot be set off
7. Loss from an exempted source cannot be set off (e.g. Share of loss of firm, agricultural income, cultivation expenses)
C) Carry forward and set off of losses
Unabsorbed loss under house property, capital loss and business loss can be carried forward for 8 years. Unabsorbed speculation business loss can be carried forward only for a period of 4 years.
Loss can be carried forward and set off even if the business in respect of which it was incurred has been discontinued. However, such loss cannot be set off against income under any other head. An exception exists in respect of unabsorbed depreciation from business which can be set off against any other source of income in the absence of business income and can be carried forward indefinitely, even if the business through which depreciation was incurred has ceased to exist.
Carry forward of losses (other than loss from house property and unabsorbed depreciation) is permissible if the return of income for the year, in which loss is incurred, is filed in time. The late filing of return should not impact the status of carry forward of loss of previous years.
When clubbing provisions apply, loss is required to be clubbed in the same manner as income. Such clubbed loss can be set off and carried forward, as if it is loss determined in the taxpayer’s own case. The successor of business can carry forward and set off the loss of his predecessor, if such succession is by way of inheritance.
In light of the above, taxpayers are advised to be mindful of the relevant provisions and seek guidance, where required, to effectively utilise their losses and achieve optimum tax results.
Conditions in brief related to carry forward and set-off of losses :-
Past year losses can be set-off against income from that respective head of income (Inter head adjustment is not possible)
(e. g. Unadjusted loss of HP for the year 2004-05 c/f Rs. 20,000. This loss can be set-off only against HP income of the year 2007-08 and not under any other head)
The above rule (1) is not applicable to unabsorbed depreciation, which can be set-off against any other head
All losses (Except loss due to owning and maintaining of race horses) can be carried forward and set-o
ff for 8 subsequent financial years following the Previous Year in which such loss arose.
Unadjusted loss due to owning and maintaining of race horses can be carried forward and set-off for 4 subsequent financial years following the Previous Year in which such loss arose.
Unabsorbed depreciation can be carried forward for an unlimited period.
D) Order of Set-off of losses
In case where profits are insufficient to absorb brought forward losses, current depreciation and current business losses, the same should be deducted in the following order
Current scientific research expenditure [Sec. 35(1)].
Current depreciation [Sec. 32(1)].
Brought forward business losses [Sec. 72(1)].
Unabsorbed family planning promotion expenditure [Sec. 36(1)(ix)].
Unabsorbed depreciation [Sec. 32(2)].
Unabsorbed scientific research capital expenditure [Sec. 35(4)].
Unabsorbed development allowance [Sec. 33A(2)(ii)].
Unabsorbed investment allowance [Sec. 32A(3)(ii)].
TO KNOW MORE ABOUT CLICK HERE TO GET PDF FILE